Dr. Glatt on Lockdowns in June 2020
Claim: Lockdowns significantly reduced covid transmission.
This is part of a series to highlight the ineptitude and sheer illiteracy of the experts my community has relied upon for covid medical advice. I am only employing arguments that can be made from the data/studies and other information available at the time the claim was made.
This rebuttal was written a few days following the publication of Dr. Glatt’s article. It has been lightly edited for grammar and clarity.
Claim: Lockdowns significantly reduced covid transmission.
Source: Rabbi Dr. Aaron Glatt COVID-19 Update, June 11, [2020] 9:00 PM
Background: Major lull in covid heading into the summer of 2020.
The Facts
Lockdowns: The Biggest Scam of the Pandemic (at the time)
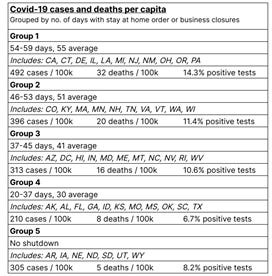
Lockdowns have been the biggest scam of the whole covid-19 pandemic. There is no data that shows any correlation between lockdowns, or lockdown severity, and superior covid outcomes at all (see above 2 charts). In fact, the correlation is precisely the opposite, as countries and states that didn’t lock down, or had less severe lockdown restrictions, tended to fare far better as far as covid went. In Italy, retrospective mathematical modeling calculated that the R-0 started decreasing before the deaths started to occur en masse (graphs on page 19 - link).
JP Morgan conducted an analysis on states and countries (link) and discovered that those that locked down had a higher rate of transmission than those states and countries that did not lock down; and they further discovered that there was a correlation between lifting lockdown restrictions and a steeper rate of declining new infections subsequently, which was even more pronounced when compared to the states and countries that did not ease lockdown restrictions.
Switzerland very famously eschewed locking down, and fared very well, in the middle of the pack of European countries; if you factor in that 70% of Sweden’s deaths were from NH’s and LTC facilities, which are unaffected by a potential lockdown, then their per capita death rate drops to Norway-level numbers. In fact, in people under 65 in Switzerland, the number of deaths from all-cause mortality is slightly less this year than the mean of the previous 5 years of all-cause mortality:
(This more than anything else demolishes entirely any notion that Sweden suffered excess deaths because of their failure to implement a lockdown.)
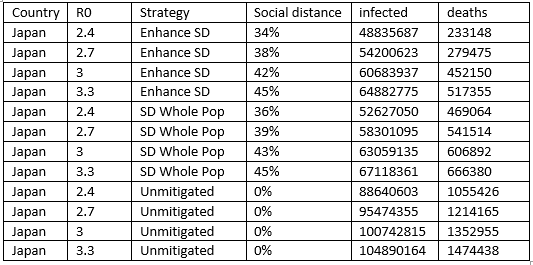
Japan didn’t lock down either, and despite having the world’s most populous and one of the most densely populated cities, (Tokyo population: 35,000,000+). Japan had a grand total of 916 deaths to date from a population of 126,476,461! That works out to 1 death for every 138,074 people. (More on this later.)
And Japan fared better than their Asian neighbors too, which means that the difference can’t be wholly attributed to demographic differences between European/American populations and Asian populations.
Here are some more examples of science against the lockdowns that was already published when Dr. Glatt wrote his article:
UK’s coronavirus lockdown was ‘futile and hasn’t saved any lives’, claim leading experts
Full lockdown policies in Western Europe countries have no evident impacts on the COVID-19 epidemic
Let’s Visualize State-by-State Shutdown Effectiveness on COVID-19
In 2007, the CDC published Community Strategy for Pandemic Influenza Mitigation, which stated
“These results suggest that the effectiveness of pandemic mitigation strategies will erode rapidly as the cumulative illness rate prior to implementation climbs above 1 percent of the population in an affected area. Thus, pre-pandemic, scenario-based contingency planning for the early, targeted use of NPIs likely provides the greatest potential for an effective public health response.”
By the time lockdowns were implemented, at least 3 months into covid-19’s invasion of American soil, the 1% benchmark had definitely been eclipsed (and just going by the initial positive test result % of 1-2% of the tests that were exclusively testing only for the upper bounds of symptomatic presentation, which as we now know is a slim minority of all cases, demonstrates this as well).
And just for kicks, here is a breakdown of US states by lockdown duration. As you can see, lockdowns did have a discernable impact on covid metrics - more lockdowns = MORE covid:
I am including a list of 50 more studies/articles on lockdowns at the end to illustrate how utterly delusional this contention was even back then.
Dr. Glatt’s junk science:
Turning to the two ‘studies’ cited by RD Glatt to support his factual assertion that lockdowns saved lives or slowed transmission.
The first one claimed that “shutdown orders prevented about 60 million novel coronavirus infections in the United States and 285 million in China”.
I attempted to figure out how they arrived at that number, but the vast quantity of data they assembled proved too insurmountable a task to bother with. Plus I couldn’t find the data, due to what I think is their tardiness in publishing it. I may be wrong about the last point and simply missed the link. In any event, I am absolutely confident that their data, which was purportedly drawn from tens if not more than 100 countries, is not capable of producing any sort of accurate result because it, and suffers from several deadly flaws:
1- Their data is not homogenous at all, as one would expect when drawing from many countries who have widely divergent cultural and legal norms, as well as societal norms, that would frustrate all but the most arduous and rigorous analysis. That would, by definition, take a dedicated research team months at least to unwind and adjust the data into a form that can be used as a matrix upon which to measure them against each other. Otherwise, all you have is a patchwork of incongruous reporting characteristics and reliability, laws, norms, enforcement mechanisms, and compliance rate, among other relevant variables that foreclose the possibility of running a comparative analysis. (This is a fairly typical type of issue that tends to invalidate a data set.)
2- It is a fait accompli that the scientists running the study engaged in some sort of data manipulation (ostensibly for the purpose laid out in the previous point), but considering the lightning speed that they ran their study, and then layering on top of that likely egregious bias, would inevitably produce a badly mangled data set that is largely divorced from the underlying data that was used to generate it.
It is axiomatically true that a Rube-Goldberg type analysis always loses when contradicted by the elementary, real-world, observed reality. And it seems to me unwise to cite a study whose foundational data is opaque to feasible review.
On to the second study cited, which comes courtesy of the now-infamous Imperial College. Simply pointing out the provenance of this one should be sufficient to invalidate it. The now-disgraced Prof. Neil Ferguson of the IC had issued another infamous model on covid, the now thoroughly trashed (debunked doesn’t begin to do it justice) IC model that predicted, among other things, that the US was staring at 2.2 million deaths, and the UK >500,000 deaths, if they eschewed lockdowns.
Mr. Ferguson is unequivocally a genuine quack and con-artist on account of his long and robust history of utterly delusional epidemiological predictions:
a. [Imperial College epidemiologist Neil] Ferguson was behind the disputed research that sparked the mass culling of eleven million sheep and cattle during the 2001 outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease. (Sheep genocide!!) He also predicted that up to 150,000 people could die. There were fewer than 200 deaths.
b. In 2002, Ferguson predicted that up to 50,000 people would likely die from exposure to BSE (mad cow disease) in beef. In the U.K., there were only 177 deaths from BSE.
c. In 2005, Ferguson predicted that up to 150 million people could be killed from bird flu. (And then he said maybe 200,000,000!) In the end, only 282 people died worldwide from the disease between 2003 and 2009.
d. In 2009, a government estimate, based on Ferguson’s advice, said a “reasonable worst-case scenario” was that the swine flu would lead to 65,000 British deaths. In the end, swine flu killed 457 people in the U.K.
Clearly, not one to be trusted. Anyway, let’s take a look at the internal machinations of this new IC study claiming that the lockdowns saved 3.2 million lives in Europe.
To begin, we must see how, exactly, they arrived at such a fantastical number (the current covid death toll worldwide stood at a comparatively paltry 430,000+ (and that’s a rather morbidly obese inflation too)).
The first thing that I noticed was that they are back to assuming the debunked 2+ million deaths in the US and 500k in the UK. Strike one (should be automatic strikeout).
Then there’s this gem:
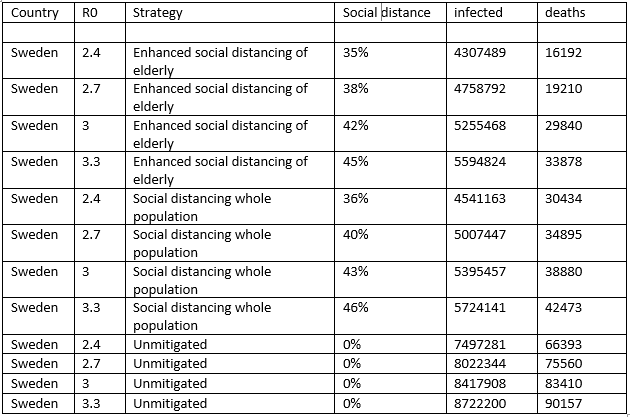
“If mitigation including enhanced social distancing is pursued, for an R0of 3.0, we estimate a maximum reduction in infections in the range 30-38% (median 33%) and a range of reduction in mortality between 19%-55% (median 39%) representing 16 million lives saved for R0=3 (assuming the mortality patterns observed in China).”
In other words, they are assuming as an input that lockdowns (“enhanced social distancing”) are effective. This effectively ends this study as useful in determining whether, a priori, lockdowns work that well in the first place, let alone if they work at all. Their assumption of R0=3.0 is soundly contradicted by their own gov’t, which was discovered to have known for quite some time already that the R0 outside of hospitals and similarly situated settings was much lower, possibly well below even 1. Whoops.
Onward. Next up is this astounding claim:
“Globally, we estimate that a completely unmitigated COVID-19 epidemic would lead to 7.0 (range 6.4-7.2) billion infections for a basic reproduction number, R0, of 3.0 (range 2.4-3.3). Applying estimates of the age-specific IFR from China, this could result in 40 (range 35-42) million deaths.”
That would make covid the most infectious virus or disease in all of human history. If that doesn’t sound fishy, I don’t know what to tell you. This is kooky. This is also refuted by all of the mortality data. For example, according to the CDC mortality data extrapolated for 100% of the US population becoming infected, the total number of deaths would be a staggering. . . 594,865 (of which 442,949 would be aged 65+). That’s not anywhere near 2.2 million (that was also assuming only 70% infection). And the 600,000 number from the CDC is based on wildly over-inflated coding for covid deaths, that has led to what we can charitably describe as peculiarities such as a bunch of gunshot victims across the country dying of covid mere hours after being shot (וכאלה רבים על זה הדרך). It seems that the only limiting factor abutting their predictive prowess is the total global human population (and even then, who knows, maybe they’ll start factoring in the deaths of babies yet to be conceived, over the next billion years, that’s a lot of babies).
Next, we have their prediction range for Sweden, which famously did not lockdown, and haven’t quite made it to 5,000 deaths yet either:
Clearly, their methods are kind of faulty…….
Here’s an even worse example:
Japan had less than 1,000 deaths to date, and they did not have any sort of lockdown whatsoever.
Note that this is the kind of “Science” that Dr. Glatt thinks is authoritative.
Clearly, this Imperial College model is as delusional as its predecessor. This is authentic scientific quackery that has no place informing policy choices. Nor is it a good look for anyone who cites it. There is more to debunk in this abomination, but I think that this is already a full-blown refutation.
In the meantime, the list of European countries that are committing to not doing another lockdown in the event of a second wave continues to grow, and now includes Denmark, Norway, England, Iceland, Ireland, and a few others. (Unfortunately, their commitments would prove to be rather noncommittal the subsequent winter.)
In Norway – that pesky country that all the experts kept using as a (false) foil to “prove” how inept Sweden was – the director of the Norway Institute of Public Health said that she thought the lockdown was a mistake and that they shouldn’t have done it.
What the actual science said:
Below are 50 published papers/articles finding that lockdowns had little or no efficacy (despite unconscionable harms) along with a key quote or two from each: (I did not put this compilation together, and unfortunately I don’t remember who did either.)
1.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.111…
“there is no evidence that more restrictive nonpharmaceutical interventions (“lockdowns”) contributed substantially to bending the curve of new cases in England, France, Germany, Iran, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, or the United States in early 2020”
“Inferences on effects of NPIs are non-robust and highly sensitive to model specification. Claimed benefits of lockdown appear grossly exaggerated.”
3.thelancet.com/journals/eclin…
“government actions such as border closures, full lockdowns, and a high rate of COVID-19 testing were not associated with statistically significant reductions in the number of critical cases or overall mortality”
4.advance.sagepub.com/articles/prepr…
“Official data from Germany’s RKI agency suggest strongly that the spread of the coronavirus in Germany receded autonomously, before any interventions become effective”
“the decline in infections in England...began before full lockdown…[S]uch a scenario would be consistent with...Sweden, which began its decline in fatal infections shortly after the UK, but did so on the basis of measures well short of full lockdown”
6.datascienceassn.org/sites/default/…
“the UK lockdown was both superfluous (it did not prevent an otherwise explosive behavior of the spread of the coronavirus) and ineffective (it did not slow down the death growth rate visibly).”
“Given that the evidence reveals that the Corona disease declines even without a complete lockdown, it is recommendable to reverse the current policy and remove the lockdown”
The end of exponential growth: The decline in the spread of coronavirusA similar pattern – rapid increase in infections to a peak in the sixth week, and decline from the eighth week – is common everywhere, regardless of response policieshttps://www.timesofisrael.com/the-end-of-exponential-growth-the-decline-in-the-spread-of-coronavirus/
“stay at home orders, closure of all non-essential businesses and requiring the wearing of facemasks or coverings in public was not associated with any independent additional impact”
“these strategies might not have saved any life in western Europe. We also show that neighboring countries applying less restrictive social distancing measures … experience a very similar time evolution of the epidemic.”
“since the full lockdown strategies are shown to have no impact on the epidemic’s slowdown, one should consider their potentially high inherent death toll as a net loss of human lives”
10.medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
“the model does not support [the] estimate that lockdown reduced the case reproduction number R by 81% or that more than three million deaths were averted by non-pharmaceutical interventions.”
11.nicholaslewis.org/did-lockdowns-…
“The case of Sweden, where the authors find the reduction in transmission to have been only moderately weaker than in other countries despite no lockdown having occurred, is prima facie evidence”
“general social distancing was also projected to reduce the number of cases but increase the total number of deaths compared with social distancing of over 70 only”
“Strategies that minimise deaths involve the infected fraction primarily being in the low risk younger age groups—for example, focusing stricter social distancing measures on care homes where people are likely to die rather than schools where they are not.”
“results presented in the report suggested that the addition of interventions restricting younger people might actually increase the total number of deaths from covid-19”
13.medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
“We show that [lockdown] is modestly superior in saving lives compared to [focused protection], but with tremendous costs to prevent one case of death. This might result in overwhelming economic effects that are expected to increase future death toll”
14.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
“For pathogens that inflict greater morbidity at older ages, interventions that reduce but do not eliminate exposure can paradoxically increase the number of cases of severe disease by shifting the burden of infection toward older individuals”
15.papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cf…
“Current policy can be misdirected and can therefore have long and even short-term negative effects on human welfare and thus result in not actually minimizing death rates (incorporating externalities), especially in the long run.”
16.imgcdn.larepublica.co/cms/2020/05/21…
“For example, the data…shows a decrease in infection rates after countries eased...lockdowns with >99% statistical significance. Indeed...infection rates have declined after reopening even after allowing for an appropriate measurement lag.
This means that the pandemic and COVID-19 likely have its own dynamics unrelated to often inconsistent lockdown measures that were being implemented.”
17.jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/…
“restrictions imposed by the pandemic (eg, stay-at-home orders) could claim lives indirectly through delayed care for acute emergencies, exacerbations of chronic diseases, and psychological distress (eg, drug overdoses).”
“In 14 states, more than 50% of excess deaths were attributed to underlying causes other than COVID-19; these included California (55% of excess deaths) and Texas (64% of excess deaths)"
18.medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
“We found that 180-day of mandatory isolations to healthy <60 (ie schools and workplaces closed) produces more final deaths if the vaccination date is later than (Madrid: Feb 23 2021; Catalonia: Dec 28 2020; Paris: Jan 14 2021; London: Jan 22 2021)”
19.papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cf…
“Comparing weekly mortality in 24 European countries, the findings in this paper suggest that more severe lockdown policies have not been associated with lower mortality. In other words, the lockdowns have not worked as intended”
“Our findings … further raise doubt about the importance in NPI’s (lockdown policies in particular) in accounting for the evolution of COVID-19 transmission rates over time and across locations”
“[the] President...has flatly denied the seriousness of the pandemic, refusing to impose a lockdown, close schools, or cancel mass events…Yet the country’s death rate is among the lowest in Europe-just over 700 in a population of 9.5 million”
22.medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
“living with children 0-11 years was not associated with increased risks of recorded SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19 related hospital or ICU admission but was associated with reduced risk of COVID-19 death (HR 0.75, 95%CI 0.62-0.92).”
23.pandata.org/wp-content/upl…
“Consistent with observations that .. lockdown has not been observed to effect the rate...of the country reproduction rates significantly, our analysis suggests there is no basis for expecting lockdown stringency to be an explanatory variable”
24.medrxiv.org/content/10.110….
“This study shows that the virus is already here, and we must find ways of living with it such that it caused no or minimal human and socioeconomic losses in ... Nigeria as a whole…. going back to the lockdown should never again be entertained”
“recruits were under the constant supervision of Marine Corps instructors. Other settings in which young adults congregate are unlikely to reflect similar adherence to measures intended to reduce transmission."
26.frontiersin.org/articles/10.33…
“The national criteria most associated with death rate are life expectancy and its slowdown, public health context (metabolic and non-communicable diseases (NCD) burden vs. infectious diseases prevalence), economy (growth national product, financial support), and environment (temperature, ultra-violet index). Stringency of the measures settled to fight pandemia, including lockdown, did not appear to be linked with death rate”
27.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.108…
“Whether a county had a lockdown has no effect on Covid-19 deaths; a non-effect that persists over time. Cross-country studies also find lockdowns are superfluous and ineffective (Homberg 2020). This ineffectiveness may have several causes. "
28.upmc-biosecurity.org/website/resour…
“There are no historical observations...that support.. confinement by quarantine of groups of possibly infected people for extended periods...The negative consequences...are so extreme…this mitigation..should be eliminated from serious consideration”
29.medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
“we present data demonstrating that mortality due to covid-19... could have been largely predicted even before the pandemic hit Europe, simply by looking at longitudinal variability of all-cause mortality rates in the years preceding the...outbreak”
30.medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
“Our analysis shows that while infection levels decreased, they did so before lockdown was effective, and infection numbers also decreased in neighbour municipalities without mandates”
31. nature.com/articles/s4159…
"After preprocessing the data, 87 regions around the world were included, yielding 3741 pairwise comparisons for linear regression analysis...we were not able to explain if COVID-19 mortality is reduced by staying at home in ~ 98% of the comparisons”
32. nature.com/articles/s4158…
"Sweden is worthy of particular attention, given...no lockdown took place.” “Notably, the estimated effectiveness of…[merely a]…public events ban in Sweden is comparable to that of lockdown in the 10 countries in which one was implemented”
33. ssbhalla.org/wp-content/upl…
"For the first time in human history, lockdowns were used as a strategy to counter the virus. While conventional wisdom, to date, has been that lockdowns were successful…we find not one piece of evidence supporting this claim.”
34. papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cf…
"on average, mandated behavioral changes accounts for only 9% (median: 0%) of the total effect on the growth of the pandemic stemming from behavioral changes. The remaining 91% (median: 100%) of the effect was due to voluntary behavioral changes”
35. bmjopen.bmj.com/content/bmjope…
"Potential determinants assessed were…the stringency index, as a measure of country-level response to COVID-19”
Results? Shotgun blast (zero correlation):
36. medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
"The decline of infections...can be attributed to relatively small interventions & voluntary behavioral changes. Additional effects of later interventions cannot be detected [&]...liberalizations of measures did not induce a re-increase of infections"
37. heritage.org/public-health/…
"The evidence suggests that, among other important findings, broad lockdown orders that fail to focus primarily on the most vulnerable members of the population—particularly the elderly—have not produced superior outcomes to less restrictive policies”
38. nature.com/articles/s4156…
"measures can substitute for a full lockdown in terms of effectiveness, while reducing adverse impacts on society, the economy, [humanity]” “Less disruptive & costly NPIs can be as effective as more intrusive, drastic, ones (eg, a national lockdown).”
39. medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
"The peculiar aspect of the claim that lockdown accounts for 81% of the reduction in R is that Sweden did not implement any lockdown, but still see a similar decrease in R as the other countries”
40. medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
"It is evident...that the growth of a COVID19 epidemic does not follow an exponential growth law even in the very first days, but instead its growth is slowing down exponentially with time...it is decelerating from the first day"
41.medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
"Japan took the atypical step of not instituting a mandatory lockdown. During this time, businesses, restaurants, & transportation were kept open, & public life continued relatively unabated. Nevertheless, the second wave peaked and subsided on its own”
42.medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
"We found no evidence that the shielding program [extreme lockdown] per se reduced COVID rates” “The effectiveness of shielding vulnerable individuals was limited by the inability to control transmission in hospital & from other adults in the household”
43. c2cjournal.ca/2021/03/do-loc…
"The stay-at-home orders...seem to have made no observable tangible impact on the daily cases & deaths. Further the most severe restrictions, such as prolonged lockdown...in California in Nov, did not prevent the subsequent spike in cases or fatalities"
44.thelancet.com/journals/lanpu…
"governments need to...apply available measures in a way that is much more targeted to different generational groups...; from March to June, 2020, 96% of additional deaths related to COVID-19 in Europe occurred in patients aged older than 70 years."
45. jclinepi.com/article/S0895-…
"We demonstrate that effects of NPIs are non-robust and highly sensitive to model specification, assumptions and data employed to fit models."
"The model proposing major benefits from lockdown in European countries had the worse fit to the data"
"Shelter-in-place [SIP] orders had no detectable health benefits, [&] only modest effects on behavior"
"We reanalyze 2 prior studies purporting...that SIP orders caused large reductions in disease prevalence & show that those results are not reliable."
"of those who reported having experienced symptoms of covid-19 in the past seven days...only 20.2%...said they had not left home since developing symptoms"
"Non-adherence was associated with...lower socioeconomic grade...and working in a key sector"
48. papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cf…
"life loss due to lockdowns themselves has never been taken into consideration"
"pro-lockdown evidence is shockingly thin & based largely on comparing real-world outcomes against dire computer-generated forecasts derived from empirically untested models"
49. medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
"All regions have peak incidence prior to the first lockdown with total incidence for England in decline well before lockdown"
"Furthermore all regions have R < 1 by either lockdown, with average R < 1 some days before either lockdown"
50. papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cf…
"social isolation at a given date showed a strong positive correlation to COVID-19 deaths 39 days later"
"strong empirical evidence that.. adoption of restrictive measures increasing social isolation have worsened the pandemic… instead of mitigating it"
Dr. Glatt would have us all believe that the debunked Imperial College model is the authoritative “science”, not the dozens and dozens of peer reviewed papers that analyzed the results and say otherwise.
In conclusion, the continuing utter failure of the current crop of so-called experts who the Rabbis have been relying upon to guide the community is something that needs to be addressed. The experts, and the medical community at large, have systematically failed to grasp the nakedly political interference that has been directing policy from the beginning. Additionally, it seems that they do not actually read data tables, much less investigate how the data put out and cited across the world is constructed and disseminated. It is unsettling to contemplate that our experts appear to be ill-informed, misguided, and seemingly lacking credible expertise informing their judgement.
I left in the conclusion to emphasize that we knew with certainty well before even June 2020 that the entire establishment narrative regarding covid was illiterate nonsense.